3D Material Guide: 3D printing with PLA Carbon Fiber Filament [2025]
- Feb 20, 2025
- 11 min read
Updated: Mar 3, 2025
3D printing technology is constantly evolving, introducing innovative materials that improve both strength and functionality. One such breakthrough is PLA-CF (carbon fiber-reinforced PLA), a filament that merges the ease of PLA printing with the rigidity and durability of carbon fiber.
This guide explores everything you need to know about PLA CF filaments: its pros and contras, comparisons to other 3D materials, best printing practices, and ideal applications. Whether you're a professional engineer, a hobbyist, or a designer looking for high-strength 3D printing materials, PLA CF might be the perfect filament for your next project.
In this guide, you will learn:
Let’s get started from the very beginning: what PLA CF filament means.

What is PLA CF Filament?
PLA CF (PLA carbon fiber filament) is a reinforced version of standard PLA, infused with carbon fibers to improve strength, rigidity, and wear resistance. Unlike regular PLA, which is known for being easy to print but relatively brittle, PLA CF filament offers increased durability and higher stiffness. The addition of carbon fiber reinforcement not only enhances structural integrity but also improves the surface finish, giving prints a more professional, matte look.
The growing popularity of PLA carbon fiber for 3D printing comes from its balance between printability and strength. While ABS filament and PETG provide better heat resistance, PLA carbon fiber stands out for its ease of printing and improved mechanical properties. As a result, it’s an excellent choice for technical parts, functional prototypes, and lightweight yet strong structures. We’ll have a look at it in more detail later.
Now let’s see how this 3D printing material is made.
How is PLA CF made?
To understand why PLA carbon fiber filament is so effective, it’s essential to look at its composition. The base material, PLA, is a biodegradable thermoplastic derived from renewable sources such as corn starch or sugarcane. It is well-known for its eco-friendly properties and ease of printing.
By incorporating finely milled carbon fibers into PLA, manufacturers create a composite filament that retains the user-friendliness of PLA while drastically improving its mechanical properties. These carbon fibers are distributed evenly throughout the filament, resulting in:
Higher rigidity and tensile strength
Increased impact resistance
Reduced warping compared to standard PLA
Sustainability of PLA CF 3D Filaments
For those concerned with sustainability, carbon fiber PLA filaments can also be produced using recycled industrial carbon fibers, further reducing environmental impact. For example, Nobufil PLAx CF Filament, which is made with 10% of carbon and 90% of recycled plastic.
Since PLA itself is biodegradable, using PLA CF filament made from recycled carbon fibers is an even more eco-conscious choice for advanced 3D printing applications. Especially considering that the parts, printed with it, look impeccable.
Just have a look at these parts, printed with Nobufil PLAx carbon fiber:
Pros and Cons of Printing with PLA carbon Filaments
While PLA CF filament offers numerous advantages over standard PLA and other materials, it also has some limitations. Check these key pros and cons, which can help you decide whether PLA carbon fiber filament is the right choice for your 3D printing needs.
Pros of PLA CF Filament
Here are the advantages of carbon fiber PLA filaments:
✔ Increased Strength and Rigidity – The infusion of carbon fibers significantly enhances the tensile strength of PLA carbon fiber, making it ideal for functional parts, mechanical components, and load-bearing structures that need extra durability.
✔ Lightweight Yet Strong – Despite its increased rigidity, PLA CF remains lightweight, thanks to the low density of carbon fibers. This makes it particularly useful for drone components, RC parts, and automotive prototypes where weight reduction is crucial.
✔ Improved Heat Resistance – Compared to regular PLA material, PLA carbon fiber filament offers better thermal stability. It allows prints to withstand higher temperatures without softening or deforming. Nevertheless, it may not match PETG or ABS filaments in heat resistance, this 3D material is still an excellent choice for those who need enhanced durability without compromising printability.
✔ Enhanced Surface Finish – One of the biggest advantages of PLA carbon fiber filament is its matte, smooth finish, which reduces the visibility of layer lines. This is particularly beneficial for visible components, prototypes, and professional-grade prints where aesthetics matter.
✔ Ease of Printing Compared to Other High-Performance Materials – Unlike 3D materials like ABS or Nylon, PLA CF prints with minimal warping, making it easy to handle. It does, however, require a hardened steel nozzle due to the abrasive nature of carbon fibers.
As you see this 3D printer material offers quite a lot of advantages. However, PLA reinforced with carbon fiber offers several disadvantages too.
Cons of PLA CF Filament
❌ Requires a Hardened Steel Nozzle – Because carbon fiber-infused filaments are abrasive, 3D printing with PLA CF will wear down standard brass nozzles quickly. A hardened steel or ruby-tipped nozzle is necessary to maintain print quality and nozzle longevity.
❌ Higher Cost Compared to Standard PLA – PLA CF filaments are typically more expensive than standard PLA due to the addition of carbon fibers and specialized manufacturing processes. However, the performance benefits often justify the cost for professional and industrial applications.
❌ Not as Flexible as PETG or Nylon – While PLA carbon fiber is much stronger than standard PLA filament, it is more brittle than PETG or Nylon. This makes it less ideal for parts that require significant flexibility or impact resistance.
❌ Limited Heat Resistance Compared to ABS or ASA – While PLA CF offers better thermal stability than regular PLA, it still falls short compared to ABS or ASA 3D material, which are better suited for high-temperature environments.
Applications for PLA Carbon Fiber Filaments:
What is PLA CF good for?
PLA CF filament is ideal for printing parts that require high strength, durability, and a professional appearance while maintaining ease of use. Consider PLA carbon fiber filaments for:
Functional Prototypes & Mechanical Parts – deal for gears, brackets, hinges, and enclosures where higher strength is needed compared to standard PLA.
Aerospace & Automotive Applications – PLA CF is commonly used for drone frames, lightweight mounts, and interior automotive components where reduced weight is a benefit.
Aesthetic & Professional Prints – The matte finish and smooth texture make PLA CF great for product enclosures, camera rigs, and architectural models.
RC & Hobbyist Projects – Commonly used in RC car parts, robotics, and custom functional tools where stiffness and precision are required.
However PLA CF offers excellent rigidity and strength, it is not as flexible as PETG or Nylon and does not have the high-temperature resistance of ABS or ASA. If those factors are crucial for your application, an alternative filament may be a better choice
How to Print PLA CF – Best Practices & Settings
3D printing with PLA CF filament requires specific settings and considerations to ensure high-quality prints while avoiding common pitfalls. Here’s what you need to know:
Recommended Nozzle Type
Use a hardened steel or ruby-tipped nozzle – PLA with carbon fiber filament is highly abrasive, and a standard brass nozzle will wear out quickly.
Recommended nozzle size: At least 0.4 mm or larger to prevent clogging from carbon fiber particles.
Ideal Print Temperatures & Cooling Settings
Extruder Temperature: 200-230°C, depending on your specific PLA CF filament brand.
Bed Temperature: 50-70°C to improve first-layer adhesion.
Cooling Fan: Off for the first few layers, then at 50-100% depending on overhangs and bridging requirements.
However, the printing settings may vary from brand to brand. Make sure to follow the recommendation that filament manufacturer provides.
Best Bed Adhesion Techniques
Use a heated glass bed, PEI sheet, or textured build surface to ensure proper adhesion.
Apply glue stick, hairspray, or a thin layer of Magigoo if adhesion issues persist.
Print slower for the first layer to improve adhesion and prevent warping.
How to Avoid Clogging & Wear on Your Printer
Use a direct drive extruder for better filament control, though a well-tuned Bowden setup can also work.
Regularly check your nozzle for wear and replace it as needed.
Keep filament dry – Store PLA CF 3D filaments in a sealed container with silica gel to prevent moisture absorption, which can lead to poor print quality.
Tip: Learn more about how to store your filaments in this guide.
Common Issues When Printing PLA CF & How to Fix Them
Even experienced users may encounter challenges when printing PLA CF filament. Here are the most common problems and how to solve them:
1. Nozzle Wear & Clogging
✅ Issue: Carbon fiber particles are abrasive and can wear down standard brass nozzles, leading to inconsistent extrusion or clogging.
🔧 Solution: Always use a hardened steel, tungsten, or ruby nozzle and clean it regularly using a cold pull method or a specialized nozzle cleaning filament.
2. Layer Adhesion Problems
✅ Issue: Poor bonding between layers can weaken the final print, especially at lower temperatures.
🔧 Solution: Increase print temperature (within safe limits) and reduce cooling fan speed for better layer bonding.
3. Warping & Bed Adhesion Failures
✅ Issue: PLA CF may experience slight warping, especially with larger prints.
🔧 Solution: Ensure the bed is properly leveled and use a heated bed (50-70°C) with an adhesive solution like PEI sheets, glue stick, or blue painter’s tape.
4. Over-Extrusion or Under-Extrusion
✅ Issue: Carbon fibers can cause inconsistencies in filament flow, leading to poor surface quality.
🔧 Solution: Perform extruder calibration, ensure your filament is dry, and use a slightly higher retraction setting than for regular PLA.
Comparison of PLA CF with other 3D printing materials
Now when you understand this 3D printer material better, let’s have a quick overview of PLA carbon fiber filament and its popular alternatives.

PLA CF vs. Regular PLA – What’s the Difference?
Which 3D material to choose: PLA or PLA carbon fiber? Let's have a look at it:
Mechanical Strength Comparison
PLA CF is significantly stronger and stiffer than regular PLA material due to the infusion of carbon fibers. This makes it better suited for functional parts and load-bearing applications. However, standard PLA is more suitable for decorative prints and non-structural components.
Printability and Nozzle Requirements
PLA CF requires a hardened steel nozzle due to the abrasiveness of carbon fibers, whereas standard PLA can be printed with a regular brass nozzle.
Standard PLA is slightly easier to print as it does not require special nozzle considerations.
When to Choose PLA vs. PLA CF
Choose PLA for simple prints, prototypes, and aesthetic parts where mechanical properties are not crucial.
Choose PLA CF for stronger, more durable components that require rigidity and better impact resistance.
PLA CF vs. PETG – Is PLA CF stronger than PETG?
PETG filaments are the second most popular 3D material choice after PLA. But is PLA reinforced with carbon fiber stronger than PETG? When to use PETG and PLA CF? Find the answers here:
Strength and Durability Comparison
PLA CF is stiffer and stronger, while PETG is more impact-resistant and flexible. If a print requires some level of flexibility, PETG might be a better option.
Heat Resistance and Flexibility
PETG withstands higher temperatures than PLA CF, making it better suited for applications that require higher thermal resistance.
Printability and Adhesion Differences
PETG filaments tend to have better layer adhesion, reducing the risk of breaking under stress.
PLA CF offers a matte finish and minimal warping, making it easier to print.
PLA CF vs. PETG CF – Which One Should You Use?
Even though, both of these 3D materials are reinforced with carbon fiber, they, of course, differ in a couple of ways. You need to know the following things when you choose among these 3D filaments:
Strength and Durability Comparison
PLA CF is stiffer and holds shape better, while PETG CF offers higher impact resistance and better flexibility. PETG CF is ideal for applications needing shock absorption, while PLA CF is suited for structural parts requiring rigidity.
Heat Resistance and Flexibility
PETG CF withstands higher temperatures than PLA CF, making it better for outdoor or heat-exposed parts, but is also not that good as ASA CF in terms of these purposes.
PLA CF, while more rigid, is less flexible than PETG CF, making it less suited for bendable components.
Printability and Adhesion Differences
PETG CF provides stronger layer adhesion, reducing the risk of delamination under stress.
PLA CF prints with minimal warping and better dimensional accuracy, making it easier for precision prints.
TIP: Learn more about PETG carbon fiber in this guide on 3D printing with PETG CF.
PLA CF vs. ABS – Strength, Durability & Printability
Another popular 3D printing material is ABS. How is it different from PLA carbon fiber material? Here is a short overview:
ABS’s Heat Resistance vs. PLA CF’s Ease of Printing
ABS withstands higher temperatures and is more resistant to outdoor conditions.
PLA CF is easier to print as it does not require an enclosed chamber like ABS. Unlike you print with Nobufil ABSx filament, which is a modified ABS and bring excellent printing result when printing without enclosures too.
Warping and Bed Adhesion Considerations
ABS tends to warp significantly, requiring a heated bed and an enclosure. PLA CF warps much less, making it easier to print successfully.
When to Use ABS vs. PLA CF Filaments
Use ABS for high-heat applications and impact-resistant parts.
Use PLA CF for high-strength, easy-to-print components with a professional finish.
TIP: Learn more about 3D printing with ABS in this guide.

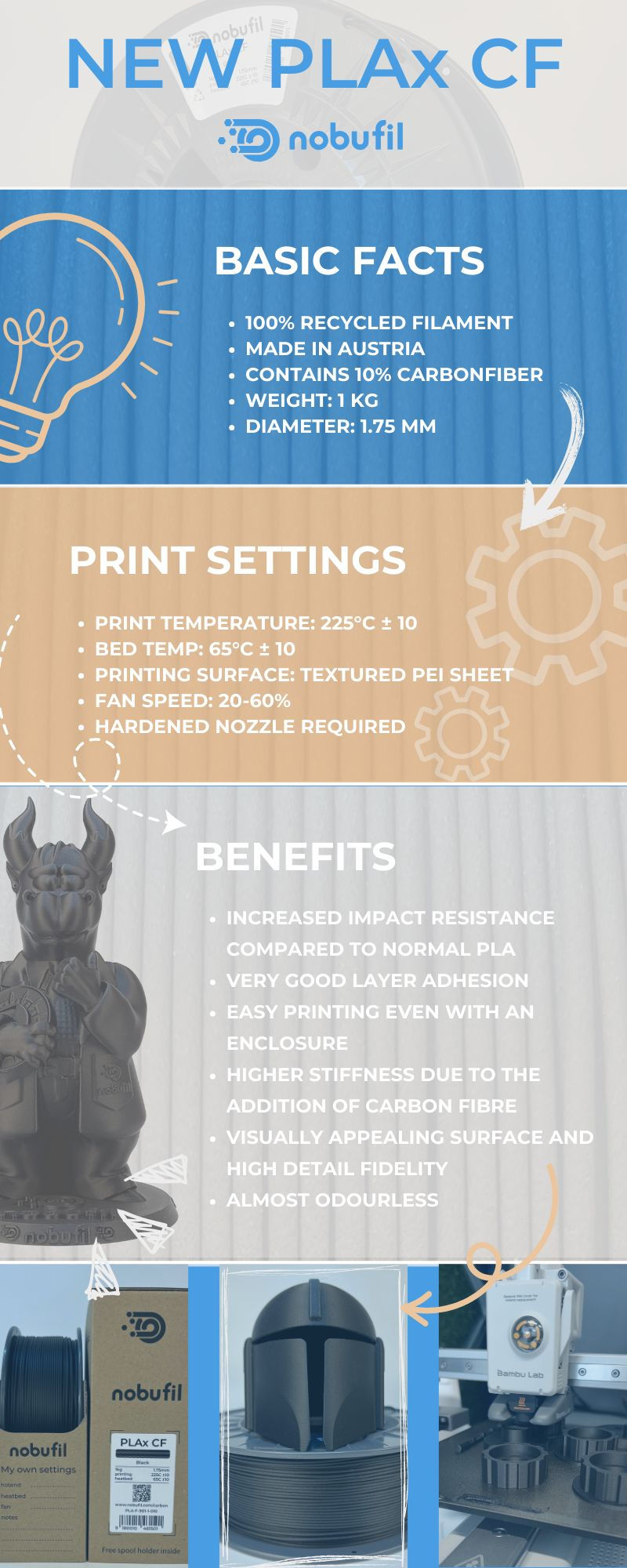
Recycled PLA CF: What is PLAx CF?
Nobufil is an Austrian filament manufacturer that recycles industrial waste and manufactures 3D printer filaments all-in-house. It is worth mentioning that all of their filaments are sustainable. Sometimes it’s difficult to believe in it, especially when looking at the printing process and its result. Recently, they enriched their sustainable 3D material range with a new material - recycled PLAx carbon fiber.
Nobufil PLAx CF is a modified PLA made from recycled industrial waste sourced in Europe, which is reinforced with 10% of carbon fiber. Thanks to its impact modification, Nobufil PLAx CF offers increased tear and break resistance similar to ABS, while maintaining the typical printing properties known from PLA.
In terms of the applications for this 3D printing material, PLAx carbon fiber filament can be used for decorative or technical parts like functional prototypes, enclosures or other parts with demand on higher impact resistance. Besides, you can use it for printing functional prototypes that need better durability than regular PLA but still require easy printability.
Nobufil PLAx CF Filament Highlights:
⚙️ Increased impact strength compared to regular PLA
⚙️ Very good layer adhesion
⚙️ Easy to print without enclosure
⚙️ Greater rigidity due to the addition of carbon fiber
⚙️ Visually appealing surface and high details
⚙️ Almost odorless in printing
⚙️ Low warping
Printing settings for Nobufil PLAx Carbon Fiber:
Here are the print settings for it, recommended by the manufacturer:
- Print temperature: 225°C ± 10
- Bed temp: 65°C ± 10
- Printing surface: textured PEI sheet
- Fan speed: 20-60%
- Hardened nozzle required
Nobufil carbon fiber PLA filament is a great sustainable option for regular PLA CF filaments, which keeps its best technical properties and offers a super easy printability.
Conclusion
To sum it up, PLA carbon fiber is an excellent 3D material choice for anyone who is seeking for a balance between strength, printability, and aesthetics. It is significantly stronger than regular PLA. Even though it requires a hardened steel nozzle and careful printing conditions, the benefits of PLA carbon fiber far outweigh its minor limitations.
For makers, engineers, and professionals, PLA CF is easy to print and is yet a highly durable solution for a wide range of applications. For example, for strong structural parts, precision models, or high-end aesthetic pieces.
We hope this guide was helpful and you learned more about this 3D material reinforced with carbon fiber.

FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions
What is PLA CF?
PLA CF (PLA carbon fiber filament) is a reinforced version of standard PLA, infused with carbon fibers to improve strength, rigidity, and wear resistance. It maintains PLA’s ease of printing while offering significantly better mechanical properties.
What are the benefits of using PLA CF filament?
PLA carbon filament offers enhanced strength, rigidity, and a matte surface finish, making it ideal for functional prototypes and structural components.
Is PLA carbon fiber suitable for outdoor use?
PLA CF material is stronger than standard PLA but shares similar vulnerabilities to heat and UV exposure, making it less ideal for prolonged outdoor applications.
Does carbon fiber reinforcement improve PLA's heat resistance?
Carbon fiber reinforcement primarily enhances strength and rigidity but does not significantly improve heat resistance.
What print settings are recommended for PLA CF filament?
It's advisable to use a hardened steel nozzle (0.6mm or larger), adjust print speeds to accommodate the filament's characteristics, and ensure proper bed adhesion to achieve optimal results with PLA-CF.
What are the common applications of PLA carbon fiber filament?
PLA CF is commonly used for creating functional prototypes, drone parts, automotive components, and tooling fixtures due to its enhanced mechanical properties.






![Ultimate Guide on 3D Printing with ABS Filaments and its Variations [2024]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/c9047f_08a1fde67547452099e746de11c5df55~mv2.jpg/v1/fill/w_980,h_551,al_c,q_85,usm_0.66_1.00_0.01,enc_avif,quality_auto/c9047f_08a1fde67547452099e746de11c5df55~mv2.jpg)

![PETG 3D Printing: Everything You Need to Know About PETG Filament [2023]](https://static.wixstatic.com/media/c9047f_ef298ec8ccd24a53882750f7f7aab48a~mv2.png/v1/fill/w_980,h_551,al_c,q_90,usm_0.66_1.00_0.01,enc_avif,quality_auto/c9047f_ef298ec8ccd24a53882750f7f7aab48a~mv2.png)
Comments